Large Push-Pull Solenoid, 9-12V
Large solenoid Push-Pull
Payments are secured by LyraCollect, a French payment collection company.
It is possible to delivered to your home, to a pick-up point or picked up by appointment at MCHobby
We prepare, pack and ship your orders with great respect and care.
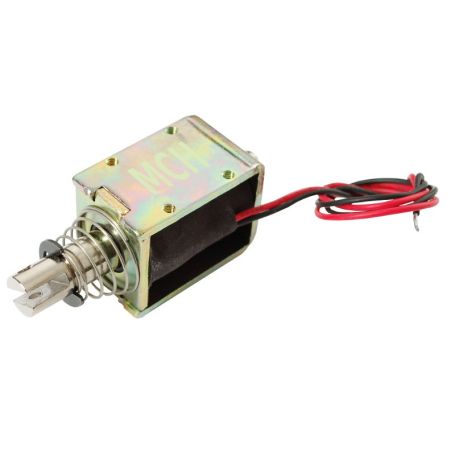
Large 9-12V DC push-pull solenoid
Basically, a solenoid is an electromagnet: it is made using a large coil of copper wrapped around a frame with a metal cylinder flowing freely in the center of the coil. The metal cylinder is drawn to the center of the coil when it is energized. This allows the solenoid to pull ("pull" from one end) or to push ("push" from the other end).
This solenoid is rather nice with its still reasonable size for a much higher power (compared to our small solenoid). It has a 40mm long body and a captive frame (which traps the axis) equipped with a spring. This means that the solenoid moves the axis when it is supplied with 24V and that the return spring returns the axis to its original place when there is no more tension. It is really very practical. Many cheap solenoids are only able to push or pull the axis and have no armature trapping the axis (and the axis falls off the solenoid). Cheap solenoid also do not have a return spring.
This solenoid has 4 M3 fixing holes on its base... which makes assembly easier.
How to use
You will need a good power source to control this solenoid since a large amount of current is required to charge the electromagnet. Under 9V, the current will be about 620mA, so do not try to power it with a 9V battery!
You will need a power transistor and a diode, as for relay mounting, but more powerful. See our tutorial for more information. .
Technical details
- Operates under 24 DC (Can be used between 9 and 24 Volts DC, but the results at lower voltage are necessarily lower)
- "Push/pull" type with 10mm axis ejection
- Resistance of the coil (continuous): 14.5 ohms
- Initial force of 6 Newton (12V DC / 50% of the cycle)
- Weight: 144 grams
Tutorials
- A small tutorial in French to order a solenoid